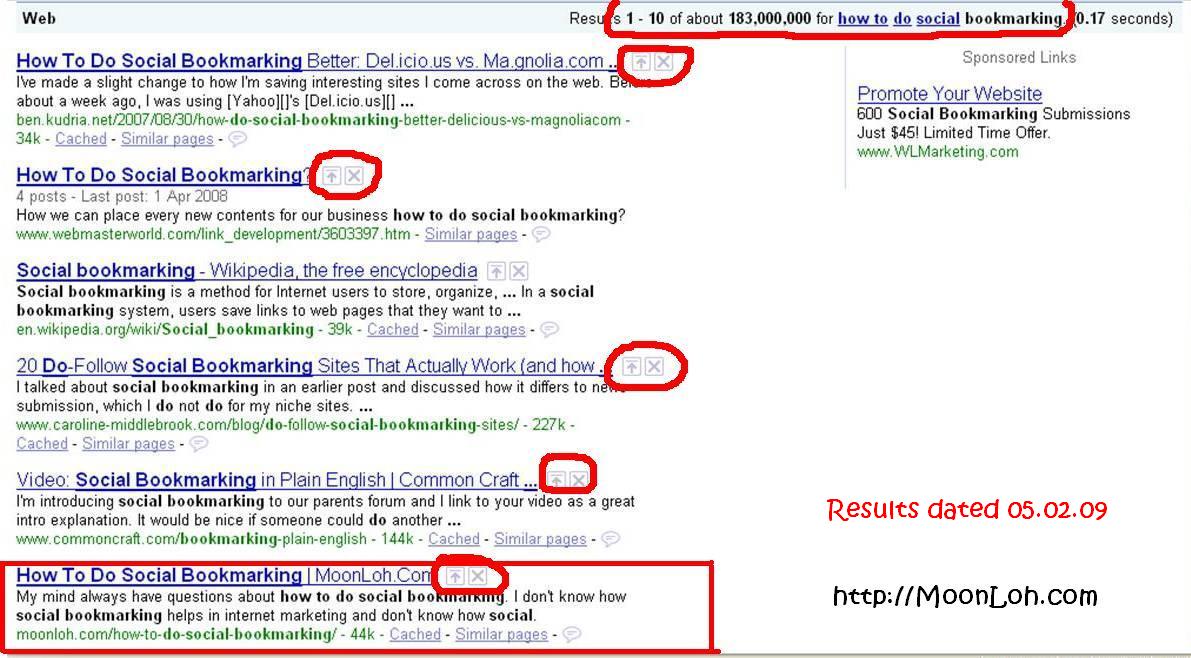
Search engine ranking factors are the factors that that can influence a web document’s rank at the major search engines for a particular term or phrase.
Search Engine Factors
A) Keyword Use Factors
B) Page Attributes
c) Site/Domain Attributes
D) Inbound Link Attributes
E) Negative Crawling/Ranking Attributes

A) Keyword Use Factors
- Keyword use in Title Tag
- Keyword use in Body Text
- Relationship of Body Text context to keywords (Topic Analysis)
- Keyword use in H1 Tag
- Keyword use in Domain Name
- Keyword use in Page URL
- Keyword use in H2, H3, H(x) Tags
- Keyword use in Alt Tags and Image Titles
- Keyword use in Bold/Strong Tags
- Keyword use in Meta Description Tag
- Keyword use in Meta Keywords Tag
B) Page Attributes
- Link popularity within the site’s internal link structure
- Quality / relevance of links to external sites / page
- Age of documents
- Amount of indexable text content
- Quality of the document content (as measured algorithmically)
- Organisation / hierarchy of document flow (i.e. broad > narrow)
- Frequency of updates to page
- Number of trailing slashes (/) in URL
- Accuracy of spelling and grammer
- HTML validation of document
C) Site/Domain Attributes
- Global link popularity of site
- Age of site
- Topical relevance of inbound links to site
- Link popularity of site in topical community
- Rate of new inbound links to site
- Relevance of site’s primary subject matter to query
- Historical performance of site as measured by time spent on page, clickthroughs from SERPs, direct visits, bookmarks, etc.
- Manual authority/weight given to site by Google
- TLD extension of site (edu, gov, us, ca, etc)
- Rate of new pages added to site
- Number of queries for site/domain over time
- Verification of site with Google webmaster centre
D) Inbound Link Attribute
- Anchor text of inbound link
- Global link popularity of linking site
- Topical relationship of linking page
- Link popularity of site in topical community
- Age of link
- Topical relationship of linking site
- Text surrounding the link
- Internal link popularity of linking page within host site/domain
- Temporal link attributes (when in time the links was created/updated)
- Domain extension of linking site (edu, gov, us, ca, etc)
- Page rank (as measured by the Google Toolbar) of linking page
E) Negative Crawling/Ranking Attributes
- Server is often inaccessible to bots
- Content very similar or duplicate of existing content in the index
- External links to low quality/spam sites
- Duplicate title/meta tags on may pages
- Overuse of targeted keywords (stuffing/spamming)
- Participate in link schemes or actively selling links
- Very slow server response times
- Inbound links from spam sites
- Low levels of visitors to the site (measured via toolbar, clicks in SERPs, etc)
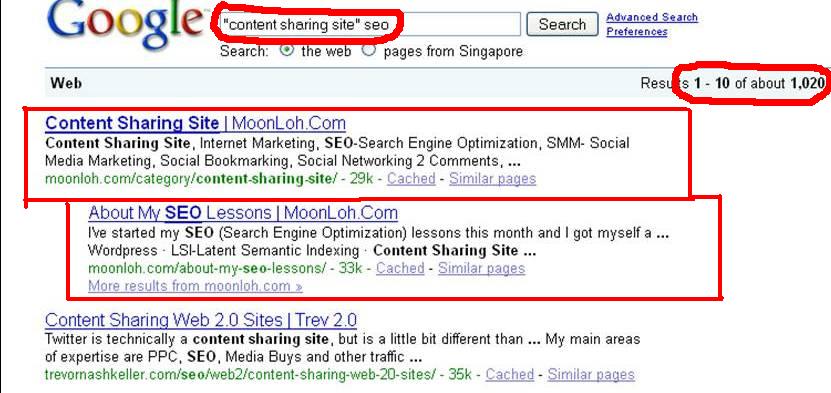
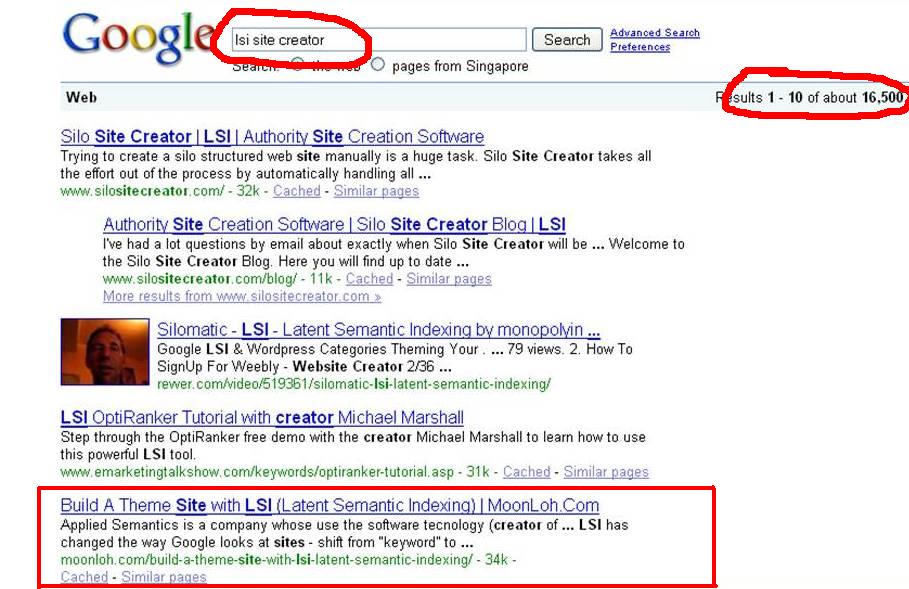
I have discussed about LSI – Latent Semantic Indexing in my previous blog post “What is LSI” but not go into detail. Today let’s see some history of LSI.
Applied Semantics is a company whose use the software tecnology (creator of CIRCA) to extract and organize information from websites in a manner similar to the way that humans might act. The software technology arose from the shortage of finding the valuable content for the advertising of Adsense ads. As you may know, Adsense ads matched the keywords on the pages to keywords in the ads and a webmaster earned money for every click he received from an ad shown on his website. Google soon found the problems of those webpages simply contain relevant keywords phrases to capture traffic for the Adsense ads without valuable content. The software technology of Applied Semantics thus plays an important role in solving this problem. In year 2003, Google purchased Applied Semantics.
The exact mathematical formula used for LSI is complicated and it analyzes pages not only for keywords, but for processing documents based on keyword themes. So its real function is to determine if the content of a site is of value to the visitor or not. Since Google found LSI technology useful and has been implementing it into its ranking algorithm, we should understand and deploy on our websites.
We have some basic knowledge about LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing), here we see how some words have other meanings to Google under the LSI.
When we perform search for the word “laptop” using Google, the returns results on the search pages are as follow:
Google BOLDS the search word “laptop”
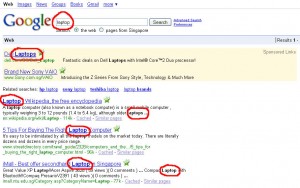
If we run a query using the LSI commands which is a ~ sign in front of the search word “~laptop”, Google will show the search results as follow:
With LSI, you can see that to Google, “laptop” also means: Dell, VAIO, Toshiba, Computers.
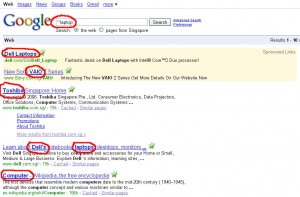
LSI has changed the way Google looks at sites – shift from “keyword” to “themes”. It based on the concept that humans are not looking for pages that contain specific keywords but for sites build around a theme.
Related post:
When most of us focus on the word SEO (Search Engine Optimization) to achive page ranking success, there is another key to page ranking success – LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing).
People always say “Content is King” and we always focus on the great content and wanted our articles to be found on search engines and therefore those articles were written with SEO in mind. Now, Let’s find out what is LSI and why it is the key to page ranking success.
LSI is Latent Semantic Indexing. It is a way for search engines to view and rank web pages in a more natural, or human manner. In other word, LSI helps search engines to find out what a web page is all about and it basically means that you shouldn’t just focus on a single keyword when optimizing our web pages and when getting links. LSI not only takes into account a keyword or phrase but also other words and phrases that are similar.
Let’s look at this example. When we want to write an article with the keyword of “buy dress”, we would include this keyword in the article about 3% for SEO purposes. However, with LSI we need to include “buy dress” a few times and also want to include other phrases like “buy clothes”, “buy long dress”, “get dress” and “purchase dress”. The article will then ranked higher in the search results because according to LSI, this article will have more value compare to only target the keyword of “buy dress”. Instead of one keyword or keyword phrase being used as anchor text, a variety of anchor text is favoured.
With the introduction of LSI, sites that previously were ranked high because of extensive inbound links based on a single keyword have now found their ranking have dropped.